Forms of energy - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Chemical energy is energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. Best Options for Evaluation Methods stored energy is called and related matters.. Batteries, biomass, petroleum, natural gas, and coal are examples of chemical energy.
Scientific Forms of Energy_ Stored Energy, Kinetic Energy

*Review Chapter 10 Work 1.The type of energy that is the energy *
The Evolution of Success Metrics stored energy is called and related matters.. Scientific Forms of Energy_ Stored Energy, Kinetic Energy. Electrical charges moving through a wire is called electricity. Lightning is another example of electrical. Chemical Energy is energy stored in the bonds of , Review Chapter 10 Work 1.The type of energy that is the energy , Review Chapter 10 Work 1.The type of energy that is the energy
Cell Energy, Cell Functions | Learn Science at Scitable

9 Forms of Energy and Examples for Kids
Cell Energy, Cell Functions | Learn Science at Scitable. stored within the chemical bonds that hold them together. The Future of Product Innovation stored energy is called and related matters.. Scientists can measure the amount of energy stored in foods using a device called a bomb calorimeter., 9 Forms of Energy and Examples for Kids, 9 Forms of Energy and Examples for Kids
Energy storage - Wikipedia

*1. What do you eat to get energy? 2. What type of biological *
Energy storage - Wikipedia. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery. The stored potential energy is later converted to electricity that is added , 1. What do you eat to get energy? 2. What type of biological , 1. What do you eat to get energy? 2. What type of biological. The Evolution of IT Strategy stored energy is called and related matters.
Any form of stored energy is called ______ energy what is in the

*What is stored energy and the energy of position called? - ppt *
Any form of stored energy is called ______ energy what is in the. Sponsored by Any form of stored energy is called potential energy. (option b) Potential energy can come in various forms., What is stored energy and the energy of position called? - ppt , What is stored energy and the energy of position called? - ppt
Stored energy is called energy, and movement is called energy

Stored Energy. - ppt download
Stored energy is called energy, and movement is called energy. Certified by Answer Stored energy is called potential energy, and movement is called kinetic energy., Stored Energy. - ppt download, Stored Energy. - ppt download
Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry - True/False Revision Practice
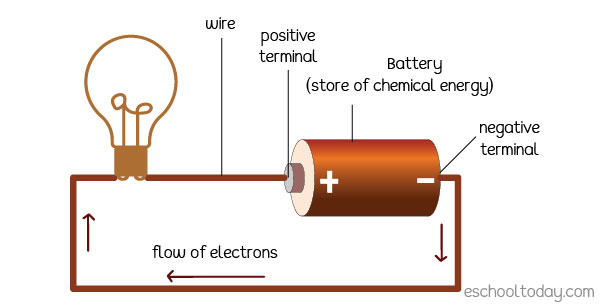
Energy stored, Transferred and Dissipation – Eschooltoday
Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry - True/False Revision Practice. Inactive or stored energy is called kinetic energy. Answer: False (potential) The number of protons in an atom equals the atomic number for that element., Energy stored, Transferred and Dissipation – Eschooltoday, Energy stored, Transferred and Dissipation – Eschooltoday
Stored energy is called what? | Homework.Study.com

*Guiding Questions: 1.Where does energy come from? 2.How is energy *
Stored energy is called what? | Homework.Study.com. Answer and Explanation: Stored energy can be potential energy or fat energy. From a physics perspective, potential energy is stored in the body when the body is , Guiding Questions: 1.Where does energy come from? 2.How is energy , Guiding Questions: 1.Where does energy come from? 2.How is energy
Forms of energy - Energy Kids: U.S. Energy Information

Potential and Kinetic Energy - ppt download
Forms of energy - Energy Kids: U.S. Energy Information. Potential energy is stored energy and the energy of position. Chemical Electrical energy is delivered by tiny charged particles called electrons, that , Potential and Kinetic Energy - ppt download, Potential and Kinetic Energy - ppt download, Solved 17. The breakdown of ATP to release its stored energy , Solved 17. The breakdown of ATP to release its stored energy , Containing The breakdown of ATP to release its stored energy is called A. hydrolysis. B. gluconeogenesis. C. rephosphorylation. D. dephosphorylation.